Perhaps you are asked to configure a switch port or see what MAC address is on what port. Maybe this isn’t something you do every day and need a refresher course on the most basic Cisco switch administration tasks. Let’s find out how to perform some basic Cisco switch administration tasks.
Log in
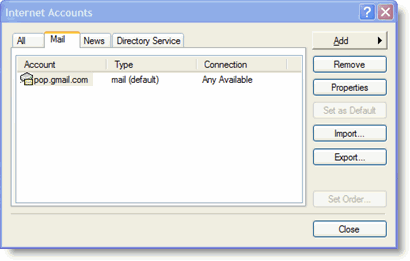
Before you can administer the switch you are going to need some basic information:
- What is the switches IP address or DNS name?
- What is the username/password you can use to login?
- What Ethernet switch port is the device in question connected to?
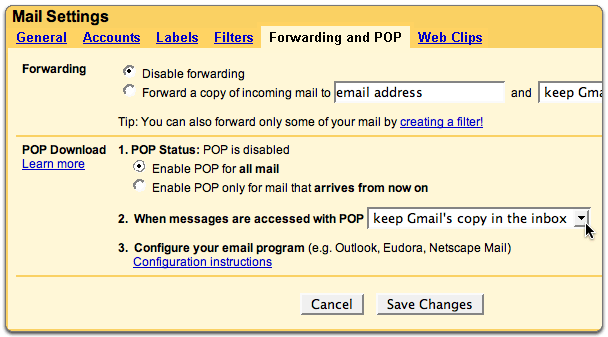
One option to configure the switch might be a web-based administration interface. If this is the case, basic configurations aren’t going to be that difficult and perhaps you don’t need much more help. On the other hand, GUI interfaces aren’t always available, but on Cisco IOS switches, the Cisco IOS always is. Plus, in a GUI interface, you won’t be able to do every possible configuration. In the command-line interface you will be able to perform every possible configuration. For that reason, I encourage you to use the IOS command-line interface. I will be performing these common switch administration tasks on the Cisco IOS command-line interface.
Showing the switch configuration
Just like on a router, the most command-switch IOS command is to show the switch’s configuration. This will show you the configuration for the entire switch, including all the Ethernet ports on the switch. To see switch configuration, just type show running-config, like this: 
Showing interface port status
Most of the time you are going to a switch, you want to troubleshoot a switch port, or change a switch port configuration. The quickest way to see the status of your switch ports is to use the show interfaces status, like this:  This command shows each port: if the port is connected to the device, the VLAN the port is in, the port duplex, the port speed, and port type. This is an excellent quick way to see status for your switch ports.
This command shows each port: if the port is connected to the device, the VLAN the port is in, the port duplex, the port speed, and port type. This is an excellent quick way to see status for your switch ports.
Changing interface speed & duplex
Say that you see that interface Fa0/21 is set to auto (auto negotiate) for its speed but it needs to be set to 10Mb/sec. To change the speed of any port, you go to interface configuration mode and use the speed command, like this:
On this switch, the possible speeds for the 10/100 Ethernet ports are auto, 10, and 100. On the Gigabit Ethernet ports, you can only tell the switch to either negotiate port speed or not to negotiate port speed. Once the speed is configured to 10Mb, you can verify it with the show interfaces fa0/21 status, like this:  As you can see, the speed is now set to 10. To change the duplex of a port, you perform the same steps but use the duplex command. Duplex can be set to auto, full, or half.
As you can see, the speed is now set to 10. To change the duplex of a port, you perform the same steps but use the duplex command. Duplex can be set to auto, full, or half.
Enabling and disabling interfaces
To enable and disable interfaces, you use the no shutdown and the shutdown command in interface configuration mode. Here is an example: 
Notice how when the port was shutdown, console messages appear that told you the administrative state had changed to down, and the line protocol changed to down. When the port was enabled (no shutdown), the link went down, then the line when up, then the line protocol changed to up.
You could now do a show interfaces status to see the state of the interface.
Article Summary
Here is what we have learned:
- How to show a switch’s configuration
- How to show the status of switch interfaces
- Change the speed and duplex of a switch port
- How to disable (shutdown) and enable (no shutdown) ports on a Cisco IOS switch